STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF BOX CULVERT
INPUTS
1. GEOMETRY
| Top width of wall | \(w_t\) |
| Bottom width of wall | \(w_b\) |
| Thickness of top slab | \(t_s\) |
| Thickness of bottom slab | \(t_b\) |
| Thickness of haunch | \(w_h\) |
| Inner width | \(B\) |
| Inner height | \(H\) |
| Depth of water inside | \(h_w\) |
| Depth of silt inside | \(h_{silt}\) |
2. GEOTECHNICAL DATA
2.1 FILL MATERIAL
| Angle of repose | \(\phi_s\) |
| Inclination of fill material | \(i_s\) |
| Soil depth above top slab | \(h_s\) |
| Water table above bottom of culvert | \(h_{wt}\) |
| Dry density of soil | \(\gamma_d\) |
| Saturated density of soil | \(\gamma_{sat}\) |
2.2 FOUNDATION MATERIAL
| Anlge of repose | \(\phi_f\) |
| Cohesion | \(c_f\) |
OTHERS
| % of passive pressure consideration | \(C_a\) |
| % of hydrostatic pressure during saturation | \(W_w\) |
| Horizontal seismic coefficient | \(A_h\) |
| Vertical seismic coefficient | \(A_v=\frac{2A_h}{3}\) |
At rest condition has been considered
Coefficient of earth pressure at rest
LOAD CALCULATION
1. For self-weight of the structure, area of section shall be calculated.
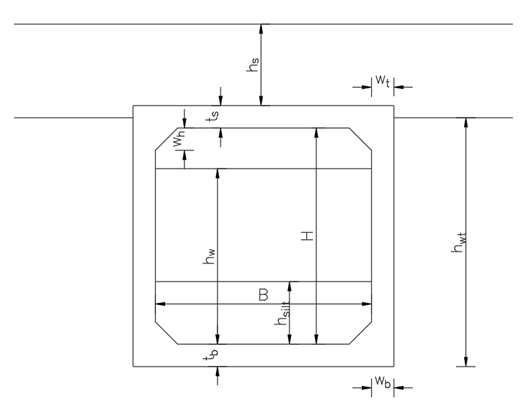
Total width of the culvert, \(B_t\)
Total height of culvert, \(H_t\)
Area of top slab
Area of wall
Area of base slab
Area of haunch
Total Area of culvert, \(A\)
Centroid of the section,\(\bar{x}\)
Centroid of the section,\(\bar{y}\)
1. CALCULATION OF LOAD INTENSITY FOR FINITE ELEMENT SOFTWARE (STAAD) INPUT
| SN | Load name | Symbol | Start value | End value | Direction | Centroid, \(\bar{x}\) | Centroid, \(\bar{y}\) |
| 1. | Self-Weight | \(F_1\) | \(F_{1s}=A×\gamma_c\) | \(F_{1s}=A×\gamma_c\) | Vertical | \(x_1=\bar{x}\) | - |
| 2. | Weight of water inside culvert | \(F_2\) | If \(h_w>H\) then \(F_{2s}=\frac{A_c×\gamma_w}{B+2w_b}\) else \(F_{2s}=\frac{\gamma_c×A_{c1}}{B+2w_b}\) Where, \(A_c=B×H-2w_h^2\) and \(A_{c1}=B×H-w_h^2\) | If \(h_w>H\) then \(F_{2e}=\frac{A_c×\gamma_w}{B+2w_b}\) else \(F_{2e}=\frac{\gamma_c×A_{c1}}{B+2w_b}\) Where, \(A_c=B×H-2w_h^2\) and \(A_{c1}=B×H-w_h^2\) | Vertical | \(x_2=\bar{x}\) | - |
| 3. | Uplift inside the culvert | \(F_3\) | If \(h_w>H\) then, \(F_{3s}=\gamma_w×(h_w-H)\) else, \(F_3=0\) | If \(h_w>H\) then, \(F_{3e}=\gamma_w×(h_w-H)\) else, \(F_3=0\) | Vertical | \(x_3=\bar{x}\) | - |
| 4. | Hydrostatic pressure inside culvert | \(F_4\) | If \(h_w>H\) then \(F_{4s}=\gamma_w×(h_w-H)\) else \(F_4=0\) | \(F_{4e}=\gamma_w×h_w\) | Horizontal | - | \(y_4=\frac{h}{3}\frac{(2F_{4s}+F_{4e})}{(F_{4s}+F_{4e})}+t_b\) Where, if \(h_w>H\) then, \(h=h_w-H\) else, \(h=h_w\) |
| 5. | Silt load inside culvert | \(F_5\) | \(F_{5s}=(\gamma_{sat}-\gamma_w)h_{silt}\) | \(F_{5s}=(\gamma_{sat}-\gamma_w)h_{silt}\) | Vertical | \(x_5=\bar{x}\) | - |
| 6. | Horizontal load due to silt inside culvert | \(F_6\) | \(F_{6s}=0\) | \(F_{6e}=k_r(\gamma_{sat}-\gamma_w)h_{silt}\) | Horizontal | - | \(y_6=\frac{h_{silt}}{3}+t_b\) |
| 7. | Weight of soil above culvert | \(F_7\) | if \((h_{wt}-H_t)\geq h_s\), \(F_{7s}=(\gamma_{sat}-\gamma_w)h_s\) elseif \( h_{wt} > H_t, F_{7s}=\gamma_d(h_s+H_t-h_{wt})+(\gamma_{st}-\gamma_w)(h_{wt}-H_t)\) else (\(h_{wt} \leq H_t\)) \(F_{7s}=\gamma_dh_s\) | if \((h_{wt}-H_t)\geq h_s\), \(F_{7e}=(\gamma_{sat}-\gamma_w)h_s\) elseif \( h_{wt}> H_t, F_{7e}=\gamma_d(h_s+H_t-h_{wt})+(\gamma_{st}-\gamma_w)(h_{wt}-H_t)\) else (\(h_{wt} \leq H_t\)) \(F_{7e}=\gamma_dh_s\) | Vertical | \(x_7=\bar{x}\) | - |
| 8. | Earth pressure | ||||||
| 8.1 | Trapezium-1 | \(F_{81}\) | If \(h_s\leq 0\) then \(F_{81s}=0\) else if \(h_{wt} <(H_t)\) then \(F_{81s}=k_r\gamma_d h_s\) else if \(h_{wt}>H_t\) then \(F_{81s}=k_r\gamma_d(h_s+H_t-h_{wt})+k_r(\gamma_{sat}-\gamma_w)(h_{wt}-H_t)\) else (\(h_{wt} \geq (H_t+h_s)\)) \(F_{81s}=k_r(\gamma_{sat}-\gamma_w)h_s\) | If \(h_{wt} \geq H_t\) then \(F_{81e}=F_{18s}+(\gamma_{sat}-\gamma_w)k_rH_t\) elseif \(F_{81e}=F_{81s}+k_r\gamma_d(H_t-h_{wt})\) | Horizontal | - | \(y_{81}=\frac{h_{81}}{3}\frac{(2F_{81s}+F_{81e})}{(F_{81s}+F_{81e})}\) where if \(h_{wt} \geq H_t\) then \(h_{81}=H_t\) else \(H_t-h_{wt}\) |
| 8.2 | Trapezium-2* | \(F_{82}\) | If \(h_{wt} \geq H_t\) or \(h_{wt}=0\) then \(F_{82s}=0\) else \(F_{82s}=F_{81e}\) | If \(h_{wt} \leq H_t\) then \(F_{82e}=F_{82s}+(\gamma_{sat}-\gamma_w)k_rh_{wt}\) else (\(h_{wt} \geq H_t\)) or \(h_{wt}=0\) then \(F_{82e}=0\) | Horizontal | - | \(y_{82}=\frac{h_{wt}}{3}\frac{2F_{82s}+F_{82e}}{F_{82s}+F_{82e}}\) |
| 9. | Hydrostatic pressure | \(F_{9}\) | If \(h_{wt} ≥ H_t\) then \(F_{9s}=\gamma_w (h_{wt}-H_t)\) else \(F_{9s}=0\) | \(F_{9e}=\gamma_w h_{wt}\) | Horizontal | - | \(y_9=\frac{h_{wt}}{3}\frac{2F_{9s}+F_{9e}}{F_{9s}+F_{9e}}\) |
| 10. | Uplift pressure | \(F_{10}\) | \(F_{10s}=\gamma_{w}h_{wt}\) | \(F_{10e}=\gamma_{w}h_{wt}\) | Vertical | \(x_{10}=\frac{B_t}{3}\frac{2F_{10s}+F_{10e}}{F_{10s}+F_{10e}}\) | |
| 11. | Seismic load-EQX | \(F_{11}\) | - | \(F_{11}=A_hF_1\) | Horizontal | - | \(y_{11}=\bar{y}\) |
| 12. | Seismic load-EQY | \(F_{12}\) | - | \(F_{12}=A_vF_1\) | Vertical | \(x_{12}=\bar{x}\) | - |
The load "Trapezium-2" can be zero if \(h_{hwt} \geq H_t\) or \(h_{wt} = 0\) that means the position of water table is either above top slab or below the base of the slab.The earth pressure shall be incorporated by "Trapezium-1".
In design of base slab of the culvert, ground reaction shall require in the calculation and can be calculated as given below.
1. Empty case
2. Full including silt
The load intensity calculated above and their position shall be carefully applied in the Finite Element software (STAAD Pro or any)
2. CALCULATION OF LOAD INTENSITY FOR STABILITY ANALYSIS
| SN | Loads | Symbol | Horizontal load, (\(H\)) | Vertical load, (\(V\)) | Lever arm, (\(\bar{x})\) | Resisting moment, (\(M_R\)) | Overturning moment,(\(M_o\)) |
| (\(kN\)) | (\(kN\)) | (m) | (\(kNm\)) | (\(kNm\)) | |||
| 1. | Self-weight | \(P_1\) | - | \(P_1=F_1\) | \(x_1\) | \(M_1=P_1×x_1\) | - |
| 2. | Weight of water inside culvert | \(P_2\) | - | \(P_2=F_2(B+2w_b)\) | \(x_2\) | \(M_2=P_2×x_2\) | - |
| 3. | Uplift of inside culvert | \(P_3\) | - | \(P_3=F_3(B+2w_b)\) | \(x_3\) | \(M_3=P_3×x_3\) | - |
| 4. | Hydrostatic force of inside culvert | \(P_4\) | \(P_4=\frac{h}{2}(F_{4s}+F_{4e})\) | - | \(y_4\) | \(M_4=P_4×y_4\) | \(M_4=F_4×y_4\) |
| 5. | Silt load inside culvert | \(P_5\) | - | \(P_5=F_5(B+2w_b)\) | \(x_5\) | \(M_5=P_5×x_5\) | - |
| 6. | Horizontal load due to silt inside culvert | \(P_6\) | \(P_6=\frac{h_{silt}}{2}(F_{6s}+F_{6e})\) | - | \(y_6\) | \(M_6=P_6×y_6\) | \(M_6=P_6×y_6\) |
| 7. | Soil load above culvert | \(P_7\) | - | \(P_7=F_7(B+2W_b)\) | \(x_7\) | \(M_7=P_7×x_7\) | - |
| 8. | Earth pressure | ||||||
| 8.1 | Trapezium-1 | \(P_{81}\) | \(P_{81}=\frac{h_{81}}{2}(F_{81s}+F_{81e})\) | - | \(y_{81}\) | \(M_{81}=P_{81}×y_{81}\) | \(M_{81}=P_{81}×y_{81}\) |
| 8.2 | Trapezium-2 | \(P_{82}\) | \(P_{82}=\frac{h_{wt}}{2}(F_{82s}+F_{82e})\) | - | \(y_{82}\) | \(M_{82}=P_{82}×y_{82}\) | \(M_{82}=P_{82}×y_{82}\) |
| 9. | Hydrostatic pressure | \(P_{9}\) | \(P_{9}=\frac{h_{wt}}{2}(F_{9s}+F_{9e})\) | - | \(y_9\) | \(M_{9}=P_{9}×y_{9}\) | \(M_{9}=P_{9}×y_{9}\) |
| 10. | Uplift pressure | \(P_{10}\) | \(P_{10}=\frac{B_t}{2}(F_{10s}+F_{10e})\) | - | \(y_{10}\) | \(M_{10}=P_{10}×x_{10}\) | \(M_{10}=P_{10}×x_{10}\) |
| 11. | Seismic-EQX | \(P_{11}\) | \(P_{11}=F_{11}\) | - | \(y_{11}\) | - | \(M_{11}=P_{11}×y_{11}\) |
| 12. | Seismic-EQY | \(P_{12}\) | - | \(P_{12}=F_{12}\) | \(y_{12}\) | - | \(M_{12}=P_{12}×x_{12}\) |
3. LOAD COMBINATION
Following load combination shall be carried out for stability analysis.
| Combination number | Load combinations |
| 1. | Dry Empty |
| 2. | Dry Full |
| 3. | Dry Empty with EQX |
| 4. | Dry Empty with EQ-X |
| 5. | Dry Empty with EQY |
| 6. | Dry Empty with EQ-Y |
| 7. | Dry Full with EQX |
| 8. | Dry Full with EQ-X |
| 9. | Dry Full with EQY |
| 10. | Dry Full with EQ-Y |
| 11. | Saturated empty |
| 12. | Saturated Full |
| 13. | Saturated empty with EQX |
| 14. | Saturated empty with EQ-X |
| 15. | Saturated empty with EQY |
| 16. | Saturated empty with EQ-Y |
| 17. | Saturated Full with EQX |
| 18. | Saturated Full with EQ-X |
| 19. | Saturated Full with EQY |
| 20. | Saturated Full with EQ-Y |
In case of dry and saturation case, the loads shall be calculated to according to depth of Water Table (WT) in above equations (2).
The stability against (i) Sliding, (ii) Overturning and (iii) Bearing stresses shall be checked for above mentioned load combinations.